Managing Metadata
Basic Metadata
If the Organization specifies its set of common metadata fields, the default view on the Metadata tab will present this form.
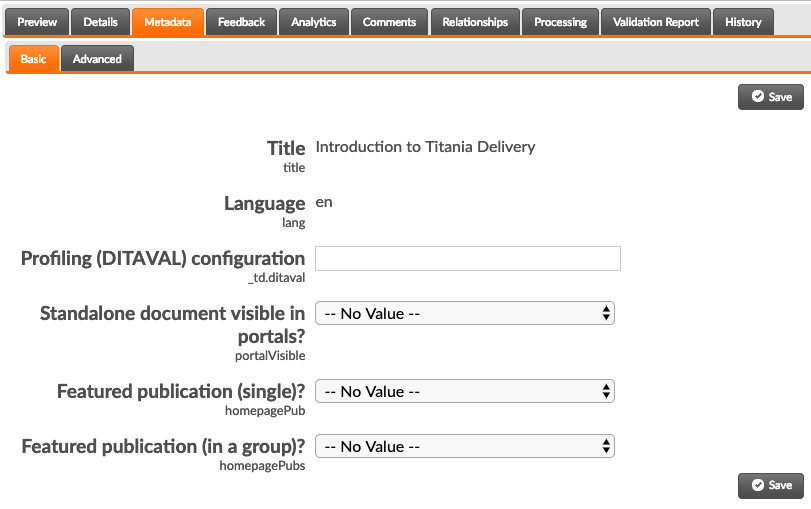
This field allows users to easily modify the values for common important metadata fields. If a user has Viewer-level access to the project, all fields will be read-only. If a field was pre-populated during content processing, meaning it is intrinsic to the contents of the file, it will also be displayed in a read-only fashion.
Advanced Metadata
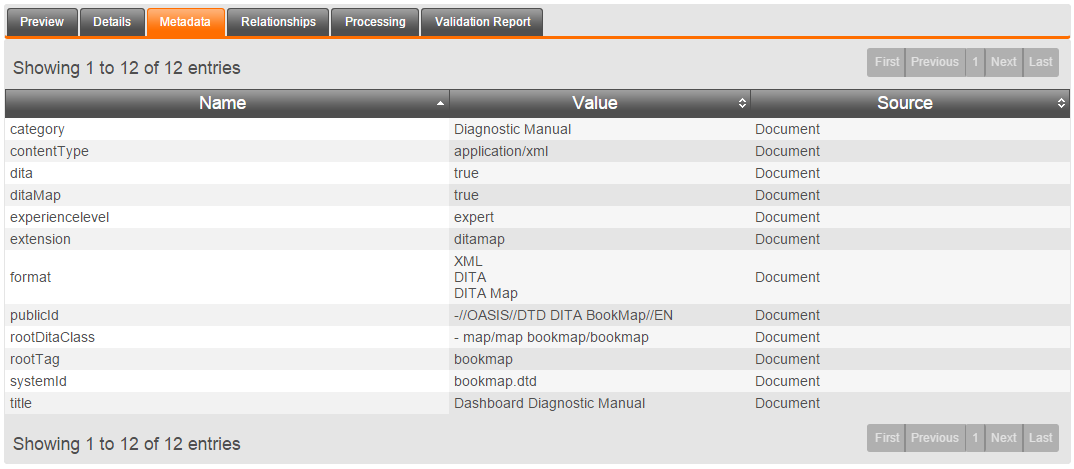
The Advanced metadata view displays all metadata on the selected file, and can be used to manually add and remove metadata values.
- On the metadata tab, click the Edit Metadata button.
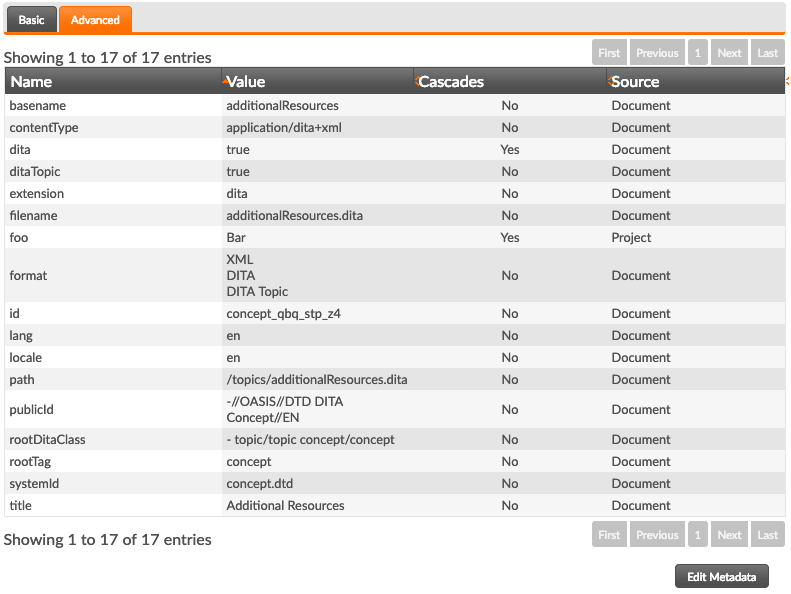
- Click the + Add button to open the Add Metadata dialog.
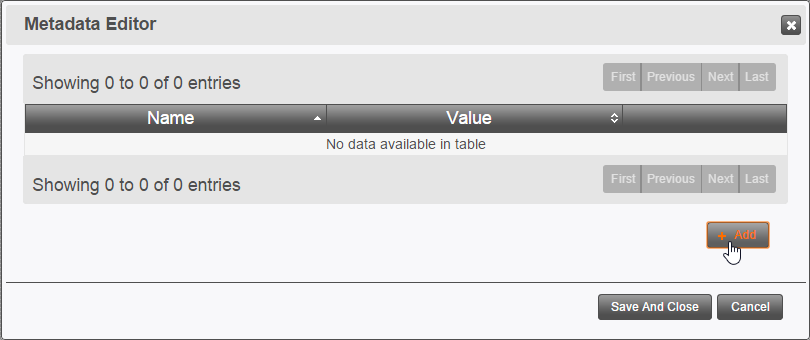
- Enter a Name and Value for the metadata.
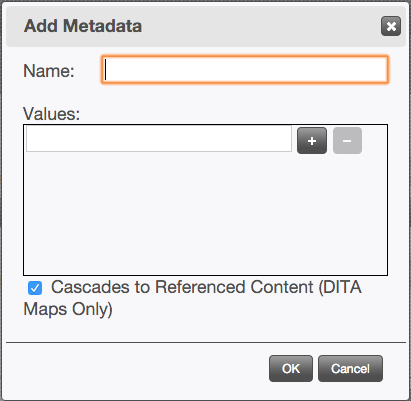
- Specify whether or not the metadata cascades. This only applies for DITA maps.
When a piece of metadata cascades, that means it is copied to the contextualized copies
of
the topics referenced by the map. For example,
titledoes not cascade, because the title of the map is not the title of its topics; but something likepublicationTypemight cascade to cover an entire logical publication. - When modifying metadata on a DITA map, use the checkbox at the bottom of the dialog to control whether the new metadata should apply to the topics referenced by the map, as well as the map itself.
Managing Metadata with CSV Files
When uploading content to a project using a Zip archive, you can include within the
zip a
file called metadata.csv containing the metadata for the files in the
archive. The rules for this CSV file are as follows.
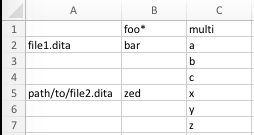
- The first row specifies the metadata keys.
- The first column specifies the file names.
- The remaining columns contain values for the metadata keys named in the first row, assigning them to the file named in the first column.
- If there is no file name in the first column, the metadata values apply to the same file as the previous row. If the previous row is completely blank, the values will not apply for any file, and will be considered "placeholders" for files to be named later.
- If a given field contains multiple values, use multiple rows for that field applying to the same file.
- If a metadata field should cascade from DITA maps to contextualized topics (see Metadata Applicability below), then the column header should end in an asterisk (*). The asterisk will not be included in the metadata name; it is simply a signifier that this field should cascade.
- Boolean values, which Microsoft Excel treats as all-caps ("TRUE" and "FALSE"), will be converted to lower-case ("true" and "false").
- The CSV file must be saved from Excel using the File Format "CSV UTF-8 (Comma-delimited) (.csv)" on the Save As... dialog.
When uploading to the system, the CSV file must be included in the Zip archive, must
be at
the root of the zip, and must be named metadata.csv. There is no harm
in the CSV file naming files that are not present in the zip; those values will be
ignored.
If the zip archive contains a folder structure, the folder path within the archive
must be
included in the file names in the first column of the spreadsheet. For example, if
there is
a file in a "topics" folder called "topic.dita", then the first column in the CSV
file for
entries pertaining to that file should be "topics/file.dita", not simply "file.dita".
Metadata Applicability
Metadata can be specified at several levels.
- Project-Level Metadata
- Metadata set on projects apply for every file in that project.
- DITA Map Metadata
- When the a metadata field is configured to cascade, it will be copied from the DITA map to the contextualized copies of referenced topics See for details.
- DITA Topic Metadata
- Metadata set on DITA topics apply to the topic by itself and to every contextualized version of that topic under all maps that reference it.
- Other Files
- Metadata set directly on other file types simply apply to that file.
Default Metadata Rules
All content automatically receives the following metadata. Unless otherwise specified, this metadata does not cascade.
filename- The name of the file.
path- The path of the file within the project, including the leading forward slash.
format- Describes the format of the content, often based on the file extension of the document. Some content, especially XML content, may have multiple values for this metadata, including values like "XML", "DITA", or "DITAMAP."
contentType- The MIME type of the content.
basename- The file's base name, before the extension.
extension- The file extension of the source file, without the leading period.
In addition, the following metadata is captured for all XML content.
publicId- The public ID of the document, if any.
systemId- The system ID of the document, if any.
schema- The
schemaLocationattribute of the default namespace of the document, if any. rootTag- The name of the root element of the document.
publicationType- This is the same as
rootTag, but unlike that entry, this one cascades from maps to contextualized topics. This allows you to filter only specific types of maps, e.g. bookmaps, using this field. dita- A boolean (true/false) entry indicating whether the content represents a DITA topic or map. Always true for DITA maps and topics, false or absent for others.
Computed Metadata for DITA Content
XML document types stored in Titania Delivery can be configured with an XSLT transform to extract metadata from XML content. The built-in DITA document types include the following rules by default.
ditaMap- A boolean (true/false) entry indicating whether the content represents a DITA map. Always true for DITA maps, false or absent for others.
ditaTopic- A boolean (true/false) entry indicating whether the content represents a DITA topic. Always true for DITA topics, false or absent for others.
rootDitaClass- The DITA @class attribute of the root element in the document, if applicable.
locale- The value of the @xml:lang attribute. If there is no
@xml:lang attribute, the default is
en. lang- If the @xml:lang attribute contains a hyphen (-), the part before the
hyphen is used. Otherwise, the full @xml:lang attribute value is used.
If there is no @xml:lang attribute, the default is
en. region- If there is an @xml:lang attribute and it contains a hyphen (-), the part of the value after the hyphen is used. No default value.
product- The @product attribute on the root element.
- The <prodname> elements within <prodinfo> elements within <prolog> (on topics) or top-level <topicmeta> (on maps).
audience- The @audience attribute on the root element.
- The @type attribute on <audience> elements within <prolog> (on topics) or top-level <topicmeta> (on maps).
experiencelevel- The @expriencelevel attribute on <audience> elements within <prolog> (on topics) or top-level <topicmeta> (on maps).
platform- The @platform attribute on the root element.
- The <platform> elements within <prodinfo> elements within <prolog> (on topics) or top-level <topicmeta> (on maps).
brand- The <brand> elements within <prodinfo> elements within <prolog> (on topics) or top-level <topicmeta> (on maps).
permission- The @view attribute on any <permission> elements within <prolog> (on topics) or top-level <topicmeta> (on maps).
category- Any <category> elements within <prolog> (on topics) or top-level <topicmeta> (on maps).
resourceid- The value of the @appid (DITA 1.3) or @id (DITA 1.2) attribute on <resourceid> elements. If the @appname attribute is also
specified, then the name of the metadata entry will be
resourceid_{@appname}with "{@appname}" replaced by the value of the @appname attribute.
The default rules will also capture <data> elements within <metadata> elements within<prolog> (on topics) or top-level <topicmeta> (on maps). The metadata name is drawn from the@name attribute, and the value is drawn from the @value attribute and the element content. If both the @value attribute is present and the element contains content, two values will be assigned to the metadata name.
Finally, the default rules will automatically capture <othermeta> elements within <prolog> (on topics) or top-level <topicmeta> (on maps). The name will be drawn from the @name attribute, and the value from @content.
Computed Metadata for DocBook Content
The built-in DocBook 5.0 document type captures the following metadata.
title- The title of the document.
locale- The value of the @xml:lang attribute. If there is no
@xml:lang attribute, the default is
en. lang- If the @xml:lang attribute contains a hyphen (-), the part before the
hyphen is used. Otherwise, the full @xml:lang attribute value is used.
If there is no @xml:lang attribute, the default is
en. region- If there is an @xml:lang attribute and it contains a hyphen (-), the part of the value after the hyphen is used. No default value.
publicationType- The name of the root element in the document, e.g.
articleorbook. - <bibliomisc>, <releaseinfo>, and <biblioid>
- When these elements appear in a top-level <info> element, the value of their @role or @class attribute will be used as the name of the metadata, and their contents as the value.
copyright-year- Each <year> within <copyright> within a top-level <info> will be represented as a distinct value of this metadata.
copyright-holder- Each <holder> in a <copyright> in a top-level <info>.
In addition, every element within the top-level <info> element that contains text only and no elements will be captured, with the metadata name being the element name, and the value being the text contents. For example, <pubdate>, <productname>, and <productnumber>.