Chapter 1: Installation
1.1: Installation
- Extract the Client Connector SDK package somewhere on your system.
-
Place the root directory of the extracted archive on your system's
PATH environment variable.
- On Windows, systems, open the Control Panel, select System and Security, select System, then Advanced system settings, and finally click the Environment Variables button on the Advanced tab. Select PATH and add the directory to the end of the value.
- On Linux or Mac OSX systems, open the
.profilefile in your home directory, creating it if it doesn't exist, and add the following.export PATH=$PATH:/path/to/harp.client-version
-
Finally, open a command prompt and execute
tdsync --help. If the usage information is printed to the console, the application has been installed correctly.
1.2: Install Server Certificate in Local Keystore
tdsync to connect to an https Titania
Delivery server, the server's certificate must be downloaded and installed in the
local java
certificate store.This document describes two different methods for installing a secure TD certificate
on a local
machine (PC, Mac, or Unix platform) in order to run tdsync. This should be
done by a system administrator. Additional third-party software applications may be
required,
depending on the method.
You'll need to know the hostname of the Titania Delivery server that you intend to connect to. That will be represented with td-host in the following examples.
Locate the java certificate store in your system's JAVA_HOME directory. This
may vary depending on your java installation, but will typically be like
JAVA_HOME/lib/security/cacerts. That location will be
represented with cacerts-file in the following examples.
Install certificate using KeyStore Explorer
KeyStore Explorer is an open-source GUI application for working with Java
keystores. It can be downloaded from http://keystore-explorer.org/. These instructions are for
KeyStore Explorer v5.4.4. Other versions may differ in some details.
- Start
KeyStore Exploreras administrator. - Select .
- Enter the td-host in the SSL Host field.
- Check Enable Client Authentication.
- Browse to cacerts-file location and enter it in the
KeyStore field.
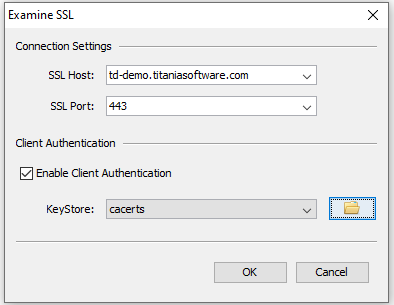
- Click OK. The Certificate Details page will appear.
- Click Import on the Certificate Details page.
- Save the cacerts-file.
- Close the
KeyStore Explorerapplication.
Install certificate using openssl and keytool
openssl is an open-source software toolkit for working with Transport Layer
Security (TLS) and Secure Sockets Layer (SSL) protocols. Source and binary distributions
can be
found from the https://www.openssl.org/ website. openssl is installed by default on
many Unix platforms.
keytool is a command-line tool that is supplied with most Java Development
Kit (jdk) installations.
- Issue the following
opensslcommand to obtain the certificate from the server. (You can name the downloaded certificate whatever you like instead of "td-cert.crt".In a Windows Powershell console, use a command like this (do not include line breaks in command):
$null | openssl s_client -showcerts -connect {td-host} 2>$null | openssl x509 > td-cert.crtIn a
bashterminal, use a command like this (do not include line breaks in command):openssl s_client -showcerts -connect {td-host} </dev/null 2>/dev/null | openssl x509 > td-cert.crt - Install the certificate (do not include line breaks in command). You can use any alias
value
(instead of "td-cert"), perhaps using the hostname of the TD
server.
keytool -import -trustcacerts -keystore {cacerts-file} -storepass changeit -noprompt -alias td-cert -file td-cert.crt